Journal of Political Risk, Vol. 1, No. 1, May 2013.
Author: Priscilla Tacujan, Ph.D.
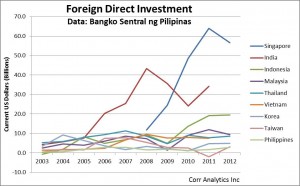
With the investment-grade credit rating granted by Fitch Ratings in March, an improved international business reputation, and sound fiscal management, the Philippines is poised to become the next foreign direct investment (FDI) destination of Asia. Other conditions for a robust investment climate are in place: a large market, skilled human capital, youthful population, and strategic location that connects population centers across Asia. Also, the Philippines is increasingly open to international trade. By 2015, Southeast Asia will have the advantage of a single market through the Association of Southeast Asian Nations Economic Community (ASEAN). According to data provided in the World Economic Forum’s Global Enabling Trade Report 2012, the country’s macroeconomic fundamentals are strong, making it attractive to at least a fraction of the foreign investors concerned over the Euro crisis.
Despite the improvement in the Philippine investment climate, the Philippine Constitution (1987) still has an antiquated article that supports laws restricting foreign ownership of property to 40% (Article XII), with minor adjustments and deviations by subsequent legislation. Removing the clause, and improving access and protections of foreign-owned business, would lead to a quantum leap in FDI and Philippine economic growth. Small changes to legislation are not enough. The Constitution needs to be changed in order to fully welcome foreign investors to the Philippines. Continue reading