Journal of Political Risk, Vol. 1, No. 8, December 2013.
By Ruge Gao
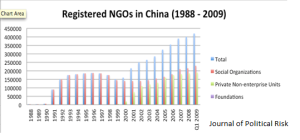
Figure 1. Registered NGOs (Civil Organizations) in China 1988 to 2009. Data source: Xu Ying and Zhao Litao, 2013.
With China’s impressive economic growth over the past few decades has come an environmental cost that reaches from the countryside to the capital.[1] While some Chinese economists believe the lack of environmental regulation encourages uninhibited growth, the Chinese State Environmental Protection Agency and State Statistics Bureau have produced statistics that indicate that environmental damages have decreased growth by three percent.[2] Triggered most prominently by the 1998 Yangtze River Floods, the number of Chinese environmental non-governmental organizations (ENGOs) began growing around 2000 and experienced explosive growth within the last decade. According to Chinese Ministry of Civil Affairs statistics,[3] in 2008 China had approximately 212,000 social groups, with 5,330 being of the environmental variety. Many Chinese ENGOs are in the public eye, but must simultaneously satisfy international donors and local government officials in order to survive. Continue reading