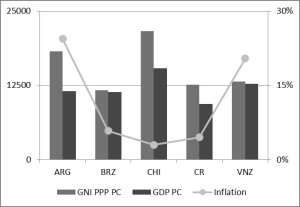
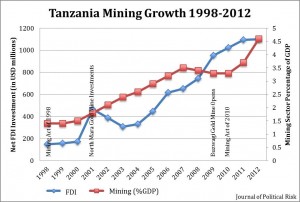
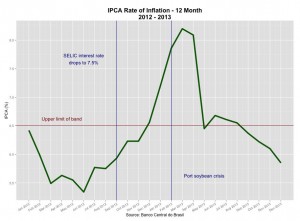
Journal of Political Risk, Vol. 1, No. 6, October 2013.
By Anders Corr, Ph.D.
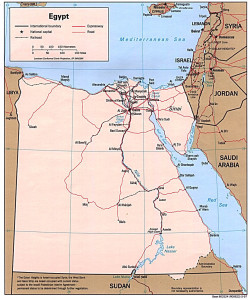
Egypt is on the verge of being engulfed by a long-term insurgency. After a brief period of democratization following the Arab Spring, the world’s most populous Arab country has returned to a popular military dictatorship. General Sisi will likely lead the country, either as power behind the President, or as President himself. The primary difference between the Egypt of Sisi and the Egypt of the pre-Arab-Spring Mubarak will be a function of the overthrow of the democratic Islamism of President Morsi. A new outraged minority with pro-democracy and pro-Islamist beliefs fielded popular protests, and was repressed with lethal force. A significant minority of that minority will now divert their energy towards terrorism and organized insurgency. Continue reading


![Figure 1: Comparison of Gambia and Sierra Leone on the Ease of Doing Business in 2013. Data Source: World Bank. [1]](https://www.canalyt.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/09/Figure-1-Gambia-Sierra-Leone-World-Bank-Ease-of-Doing-Business-2013-300x180.jpg)